Import
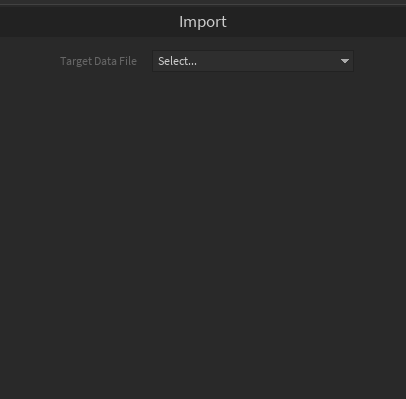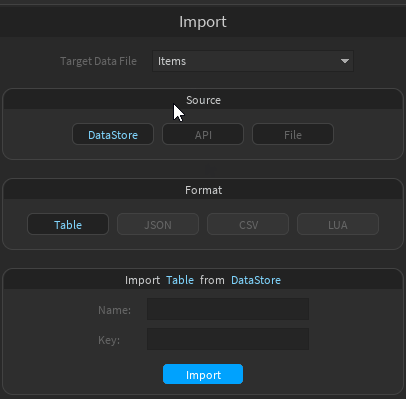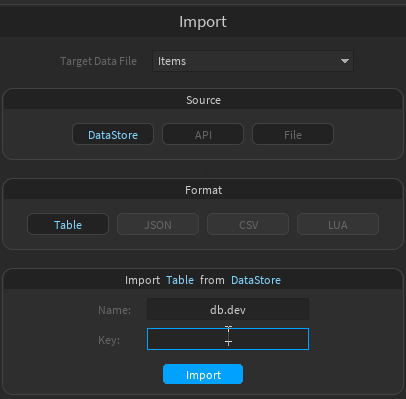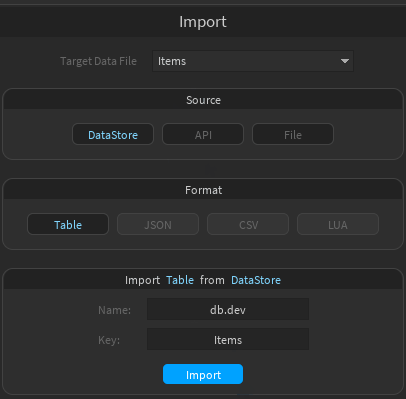
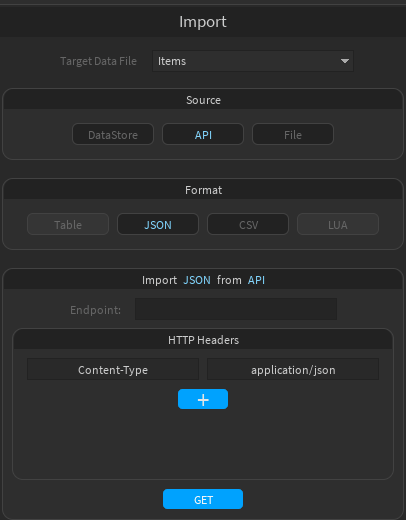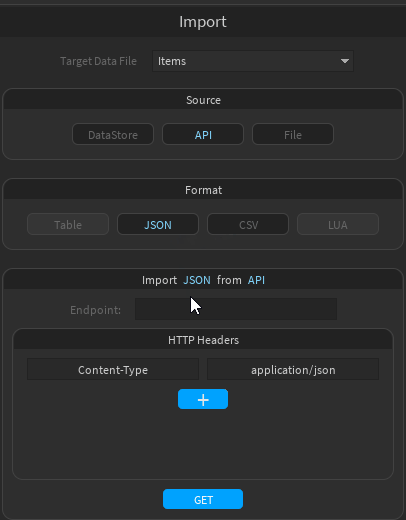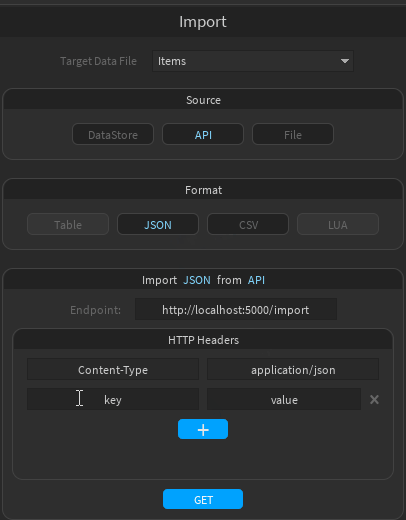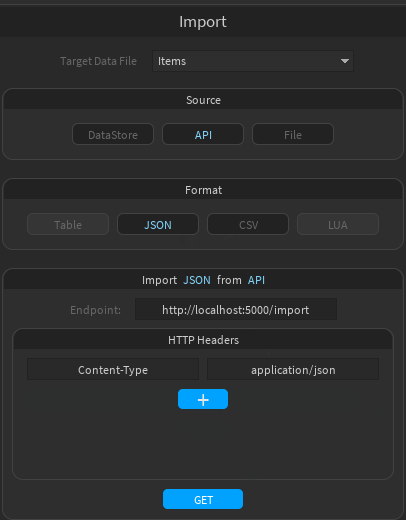
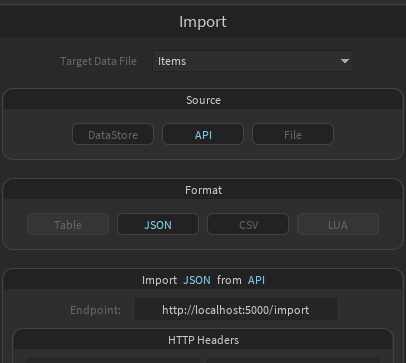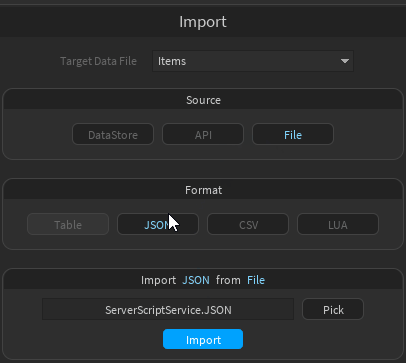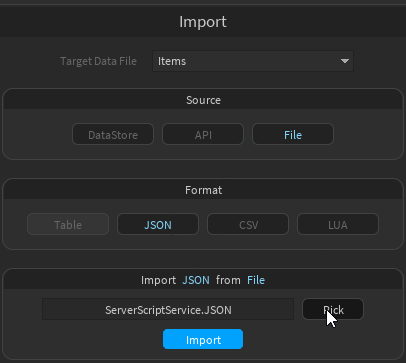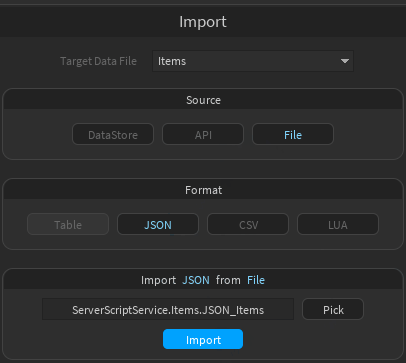
On the Import page, data files can be imported in multiple ways.
- Select a data file that you want to import data into
- Select JSON or CSV as Format
- Enter the URL of your API's import route
- Optionally, add custom HTTP headers if needed
- Click "GET"
Expected Data Example
-
JSON
-
CSV
Set up an API
If you need help creating an API, check out: Example - Google Sheets API
- Select the Format
- Select a file in the Explorer that contains the data you want to import
- Click "Pick" to set it and finally click "Import"
CSV Delimiter
The CSV delimiter can be edited in Global Settings
Side Effect...
A side effect of importing a ModuleScript is that it can essentially act as a script executor. For instance, if this were the content of the ModuleScript you’re importing:
local module = {}
local function doSomething()
print("This can be used as a script runner...")
end
doSomething()
return module
No data would be imported into the selected target data file, so it remains unchanged. However, because require() is called on the ModuleScript you’re importing, its code will execute. This allows you to run custom scripts or functions in Studio. That said, be careful not to select a file that could potentially harm your code or project when executed with require().